Assessment outcomes data and lessons learnt for the NGPA Scheme
Summary of accreditation outcomes and lessons learnt from the assessment of general practices against the RACGP Standards for general practices (5th edition) and the RACGP Standards for point-of-care testing (5th edition).
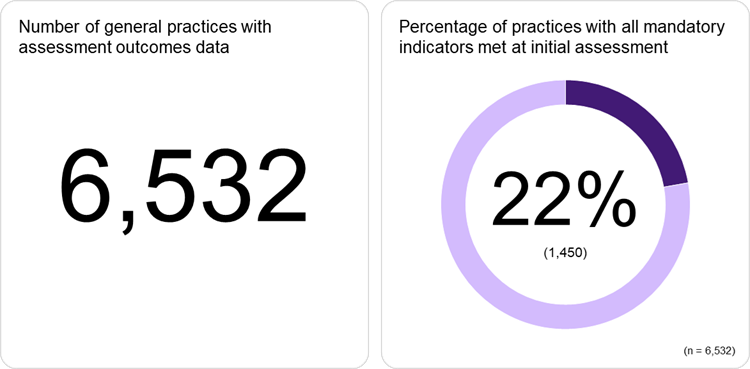
Assessment outcomes data
Australian general practices with assessment outcomes data to the RACGP Standards for general practices (5th edition) from April 2023 to January 2026.
Number of Australian general practices with assessment outcomes data to the RACGP Standards for general practices (5th edition) by state and territory, and practice type.
| Practice type |
NSW |
VIC |
QLD |
SA |
WA |
TAS |
NT |
ACT |
Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General practice |
2,047 |
1,620 |
1,312 |
412 |
628 |
123 |
52 |
94 |
6,288 |
| Aboriginal medical service |
54 |
23 |
56 |
17 |
20 |
5 |
67 |
2 |
244 |
| Total |
2,101 |
1,643 |
1,368 |
429 |
648 |
128 |
119 |
96 |
6,532 |
*Other - Cocos (Keeling) Islands, Christmas Island and Jervis Bay Territory
A repeat assessment is required when a general practice has 20% or more mandatory indicators rated ‘not met’ following the initial routine assessment. This ensures the general practice has fully embedded all the changes that were implemented to meet all mandatory indicators when it was awarded accreditation. Full requirements of a repeat assessment are stipulated in Advisory GP23/03: Standardised repeat assessment of general practices.

*Standardised repeat assessments have been implemented from 1 January 2024.
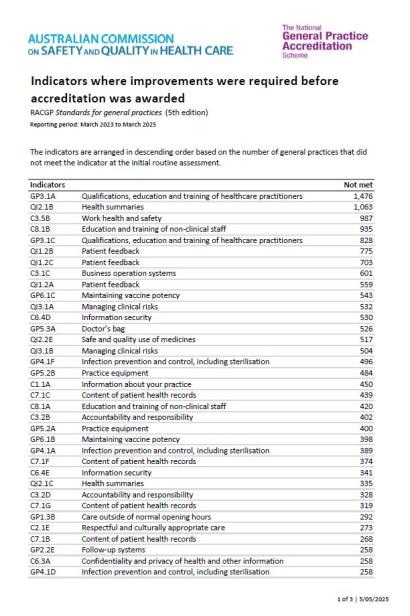
Indicators most frequently rated as ‘not met’
The below graph shows the mandatory indicators in the RACGP Standards for general practices (5th edition) that are most frequently rated as ‘not met’ at the initial routine assessment.
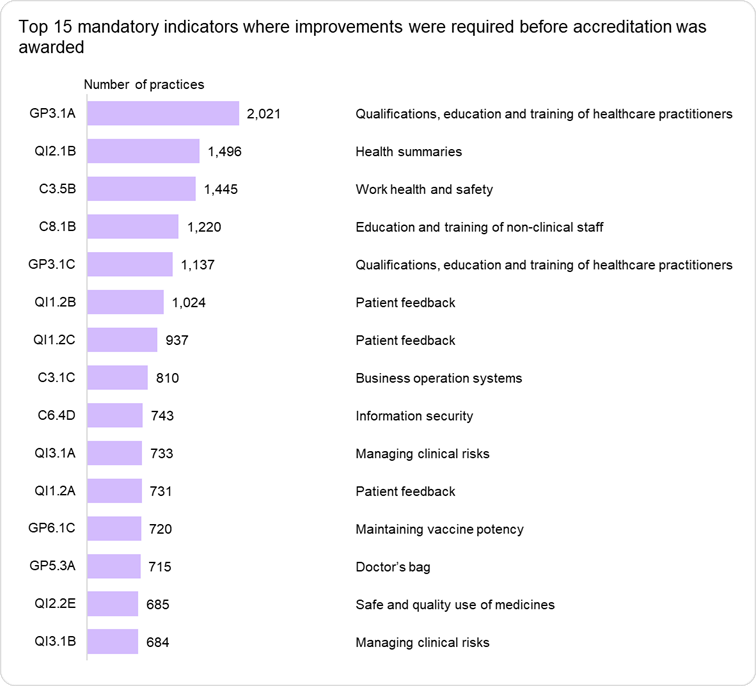
The assessment outcomes of all 125 indicators of the RACGP Standards for general practices (5th edition) are outlined in the list below.
Lessons learnt
- Mandatory indicators rated as ‘not met’ are largely consistent across general practices in major city and rural or remote locations
- For the three top indicators rated as ‘not met’, the main reason provided by assessors was ‘documentation not available’ from the general practice during the initial assessment
- Most critical issues identified during the assessment of general practices warranting escalation to healthcare complaints organisations have been in relation to:
- GP4.1 - Infection prevention and control, including sterilisation
- GP6.1 - Maintaining vaccine potency
- GP2.2 - Follow-up systems
- QI2.2 - Safe and quality use of medicines.